Today we will learn Bubble Sort Program in C. So, before getting started you should have a basic knowledge about bubble sorting in C.
Table of Contents
What is a Bubble Sort?
This is one of the simplest and most popular sorting methods. The basic idea is to pass through the elements sequentially several times (n-1) times. In each pass, we compare successive elements (x[i] with x[i+1]) and interchange the two if they are not in the required order.
One element is placed in its correct position in each pass. In the first pass, the largest element will sink to the bottom, second largest in the second pass and so on. Thus, a total of n-1 passes are required to sort ‘n’ keys.
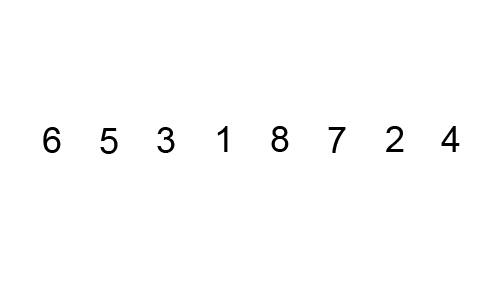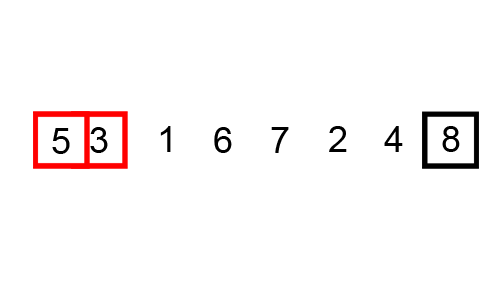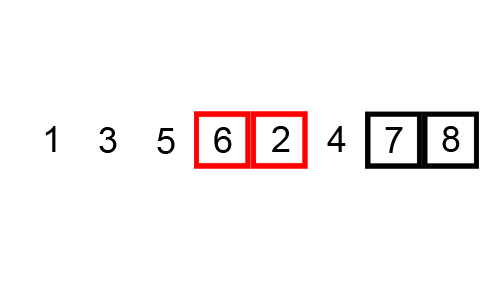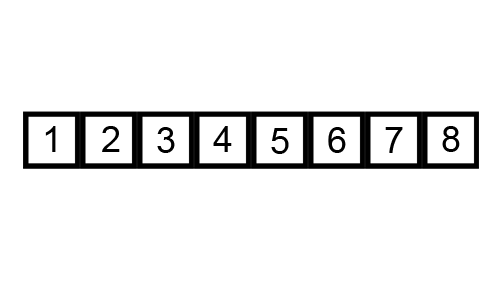
For Example: 25 37 12 48 57 33
1st Pass:

2nd Pass :

3rd Pass :
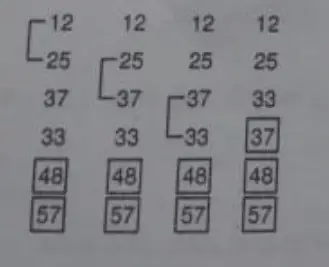
4th Pass:
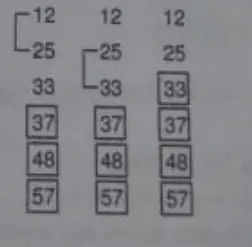
5th Pass:
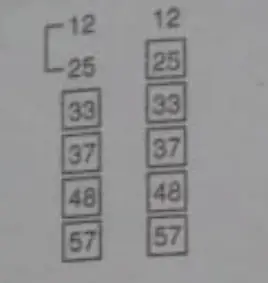
Bubble Sort Algorithm:
1 Step: START.
2 Step: Pass=1.
3 Step: i=0.
4 Step: if x[i]>x(i+1) then interchange x[i] and x[i+1]
5 Step: i=i+1
6 Step: If i<=n-1-Pass then go to step 4
7 Step: Pass=Pass+1.
8 Step: If Pass<n then go to step 3.
9 Step: STOP.
The efficiency of Bubble Sort:
There are n-1 comparisons in the first pass,n-2 in the second pass and 1 in the n-1th pass.
Therefore Total number of comparisons = (n-1)+(n-2)+…+1=n(n-1)/2.
The same number of passes is required in the best case (already sorted) and the worst case (elements in the reverse order). Hence the Best case and worst-case time complexity is O(n^2).
Advantages:
It is Simple Sorting Method.
No additional Data Structure is required.
It is in-place sorting method.
It is a stable sorting method.
Disadvantages:
It is very inefficient method-O(n^2).
Even if the elements are in the sorted order, all n-1 passes will be done.
1. Bubble Sort Program in C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[100], number, i, j, temp;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Number of Elements : \n ");
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements :\n ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
scanf("\t%d", &a[i]);
for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < number - i - 1; j++)
{
if(a[j] > a[j + 1])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("\n List Sorted in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Output:
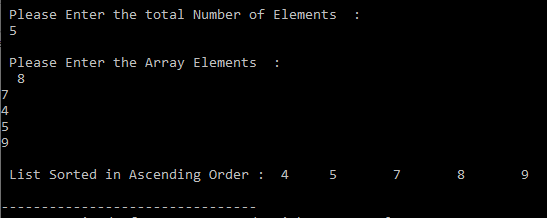
Explanation:
First For Loop: First Iteration-
for(i=0;0<4;0++) The Condition is TRUE so it will enter in the second for loop.
Second For Loop: First Iteration-
for(j=0;0<5-0-1;0++) The Condition is TRUE so the compiler will enter in the if statement.
if(a[0]>a[1])->if(8>7) It means condition is TRUE so temp=10.Now a[j]=a[j+1]->a[0]=a[1]->a[0]=7. And a[j+1]=temp->a[1]=8. So the array will become 7 8 4 5 9 and j will be incremented by 1.
Second For Loop: Second Iteration-
for(j=1;1<5-0-1;1++) the condition is TRUE so the compiler will enter into if statement if(8>4) it means the condition is TRUE.
So like this process continuously goes on.
Improving Efficiency of Bubble Sort:
It is quite possible that the array gets sorted before all n-1 passes are complete. To avoid unnecessary passes, we have to check whether the array has got sorted at the end of each pass.
This can be done by finding out if an interchange was made in a pass. If no interchanges were done, it implies that the array has got sorted. It can be checked by using a flag.
Bubble Sort Improving Efficiency Algorithm:
1 Step: START.
2 Step: Pass=1.
3 Step: swap=FALSE.
4 Step: i=0.
5 Step: If x[i]>x[i+1] then Interchange x[i] and x[i+1] and Swap=TRUE.
6 Step: i=i+1.
7 Step: If i<=n-Pass-1 then go to step 5.
8 Step: If swap=FALSE then go to step 11.
9 Step: Pass=Pass+1.
10 Step: If Pass<n then go to step 3.
11 Step: STOP.
2. Improved Bubble Sort Program
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int array[100], n, i, j, swap,flag=0;
printf("Enter number of elements \n");
scanf("\t%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d Numbers:\n", n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &array[i]);
for(i = 0 ; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for(j = 0 ; j < n-i-1; j++)
{
if(array[j] > array[j+1])
{
swap = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = swap;
flag=1;
}
if(!flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
printf("Sorted Array is :");
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("\t%d", array[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
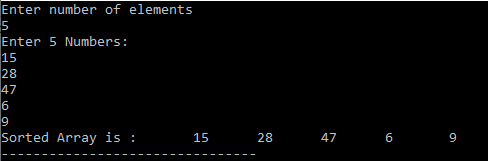
3. Bubble Sort Program Using While Loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[100], number, i, j, temp;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Number of Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
i = 0;
while(i < number - 1) {
j = 0;
while(j < number - i - 1) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
j++;
}
i++;
}
printf("\n List Sorted in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++)
printf(" %d \t", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
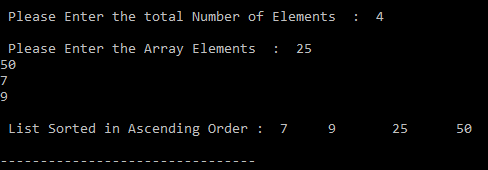
Output:
4. Bubble Sort Using Function
In this program, we will declare a user-defined function to sort an array according to the logic of Bubble Sort.
#include <stdio.h>
void bubbleSort(int a[], int number) {
int i, j, temp;
for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < number - i - 1; j++) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[100], size, i;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Number of Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &size);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
bubbleSort(arr, size);
printf("\n List Sorted in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
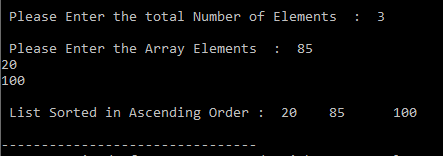
Output:
5. Bubble Sort Using Pointers in C
In this program, we will add extra function to swap two numbers using pointers in C.
#include <stdio.h>
void Swap(int *x, int *y)
{
int Temp;
Temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = Temp;
}
void bubbleSort(int a[], int number) {
int i, j, temp;
for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < number - i - 1; j++) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
Swap(&a[j], &a[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[100], size, i;
printf("\n Please Enter the total Number of Elements : ");
scanf("%d", &size);
printf("\n Please Enter the Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
bubbleSort(arr, size);
printf("\n Array Sorted in Ascending Order : ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
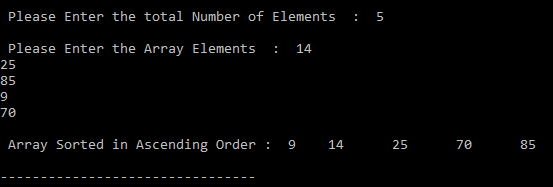
Output:
Also Read:
- C Program to Make Simple Calculator
- Armstrong Number Program in C
- Fibonacci Series Program in C
- Decimal to Binary Conversion Program in C
- Reverse a String in C
- Program to Reverse a Number in C
- Hello World Program in C
- Palindrome Program in C
- Leap Year Program in C
- Factorial Program in C
- Prime Number Program in C
- Program to print prime numbers from 1 to n
- Anagram program in C.
- Calculate LCM Program in C.
- Addition of Two Numbers in C
- Matrix Multiplication Program in C.
- Playfair Cipher Program in C.
- GCD Program in C.
- Tower of Hanoi in C.
- First Fit Program in C
- Swapping of two numbers in C
- Menu Driven Program in C.
- Odd or Even number program in C
- Round Robin Program in C
- Simple Interest Program in C
- Quadratic Equation Program in C.
- Insertion Sort Program in C.
![FIFO Page Replacement Algorithm in C [ Program With Explanation]](https://learnprogramo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/FIFO-PAGE-REPLACEMENT-ALGORITHM-IN-C-1-500x383.png)

