In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to write a menu-driven program in python using functions, while loop, and switch case. But before start writing the program we’ll first learn about menu-driven programs. What actually they are and where they’re used. So,
Table of Contents
What is Menu Driven Program in Python?
As the name suggests the menu driven program is a type of computer program which accepts the input from the user by showing a list of options. And users have to select any of the options to perform any operation. An example of a menu driven program is a washing machine which consists of menu driven programmed microprocessor.
The second example of menu driven program in python is a Simple calculator which we used to perform some calculations. If we press ‘+’ for addition then the addition of two numbers case is executed. We can also do the calculations related to mensuration i.e calculating the area of the circle, the circumference of the cylinder, etc.
Menu driven programs are beneficial in a situation where the multitasking machines can perform a single task at a time. So without wasting any time we’ll see how to write menu driven program in python.
In this tutorial, we’ll code menu driven programs in python using different ways. Let’s see them one by one:
Menu Driven Program in Python Using While Loop
In this program, we’ll write a python program to calculate the area of different shapes using a while loop.
#Learnprogramo - programming made simple
while True:
print("Menu Driven Program")
print("1.Area of Circle")
print("2.Area of Rectangle")
print("3.Area of Square")
print("4.Exit")
choice=int(input("Enter your choice:"))
if choice==1:
radius=int(input("Enter radius of Circle:"))
print("Area of Circle",3.14*radius*radius)
elif choice==2:
length=int(input("Enter length of Rectangle:"))
breadth=int(input("Enter breadth of Rectangle:"))
print("Area of Rectangle:",length*breadth)
elif choice==3:
side=int(input("Enter side of Square:"))
print("Area:",side*side)
elif choice==4:
break
else:
print("Please enter the correct choice")Output:
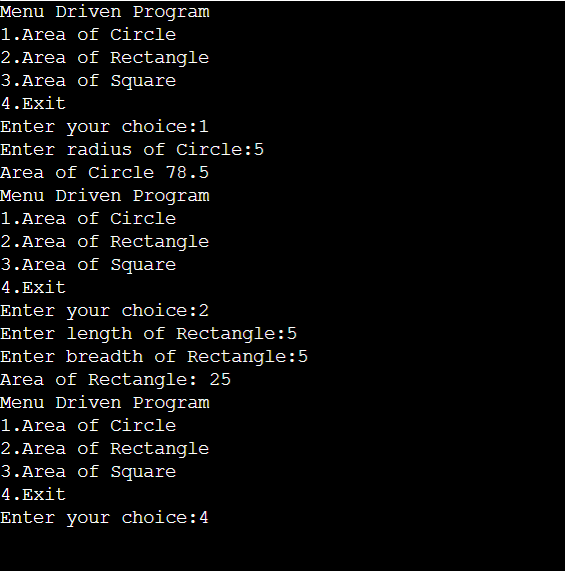
Explanation:
In the above program, we’ve used a while loop to perform menu operations. After executing the program the compiler displays the list of menu options. And then the user has to choose the option by pressing the numbers which are assigned to the menu. If the user enters 1 and selects the Area of the circle then the compiler asks the user to enter the radius of the circle and then displays the output as an area of a circle.
Similarly, after choosing the menu option 2nd the compiler asks user to enter the length and the breadth of the rectangle to calculate the area of the rectangle. And after calculating the area compiler displays the area.
If the user enters the wrong choice then the message “Please enter the correct choice” will be displayed.
By choosing menu option 4 the program will be exited.
Menu Driven Program in Python Using Functions
In this program, we’ll write menu driven program in python using functions
#Learnprogramo - programming made simple
def circle(radius):
print("Area of Circle",3.14*radius*radius)
def rectangle(length,breadth):
print("Area of Rectangle:",length*breadth)
def square(side):
print("Area:",side*side)
while True:
print("Menu Driven Program")
print("1.Area of Circle")
print("2.Area of Rectangle")
print("3.Area of Square")
print("4.Exit")
choice=int(input("Enter your choice:"))
if choice==1:
radius=int(input("Enter radius of Circle:"))
circle(radius)
elif choice==2:
length=int(input("Enter length of Rectangle:"))
breadth=int(input("Enter breadth of Rectangle:"))
rectangle(length,breadth)
elif choice==3:
side=int(input("Enter side of Square:"))
square(side)
elif choice==4:
break
else:
print("Please enter the correct choice")Output:
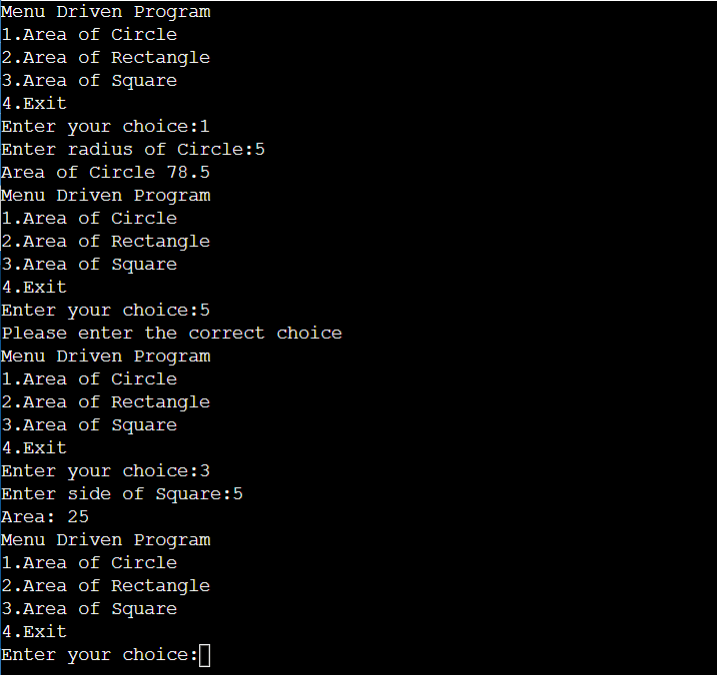
Explanation:
In the above program, we’ve used functions to write menu driven programs in python. After executing the above program the compiler will display the list of menu options. The user has to choose the option and enter it. The compiler will compare the input entered by the user and then call the function.
Suppose if the user enters input 1 then the compiler will store that input into choice and check for the condition choice==1 then the function circle will be executed. The logic of calculating the area of a circle is written in the circle function which accepts the radius as a parameter.
After calculating the area the compiler displays the desired area of the circle on the screen. If you enter the wrong choice then the compiler will print the “Please enter the correct choice” message.
After choosing menu option 4 the program will be stopped.
Menu Driven Program in Python to Build a Simple Calculator
In this program, we’ll build one simple calculator which accepts some input from the user and then perform calculations.
#Learnprogramo - programming made simple
# defining addition function
def add(a, b):
sum = a + b
print(a, "+", b, "=", sum)
# defining subtraction function
def subtract(a, b):
difference = a - b
print(a, "-", b, "=", difference)
# defining multiplication function
def multiply(a, b):
product = a * b
print(a, "x", b, "=", product)
# defining division function
def divide(a, b):
division = a / b
print(a, "/", b, "=", division)
# printing the heading
print("WELCOME TO A SIMPLE CALCULATOR")
# using the while loop to print menu list
while True:
print("\nMENU")
print("1. Addition")
print("2. Subtraction")
print("3. Multiplication")
print("4. Division")
print("5. Exit")
choice = int(input("\nEnter the Choice: "))
# using if-elif-else statement to pick different options
if choice == 1:
print( "\nADDITION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
add(a, b)
elif choice == 2:
print( "\nSUBTRACTION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
subtract(a, b)
elif choice == 3:
print( "\nMULTIPLICATION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
multiply(a, b)
elif choice == 4:
print( "\nDIVISION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
divide(a, b)
elif choice == 5:
break
else:
print( "Please Provide a valid Input!") Output:
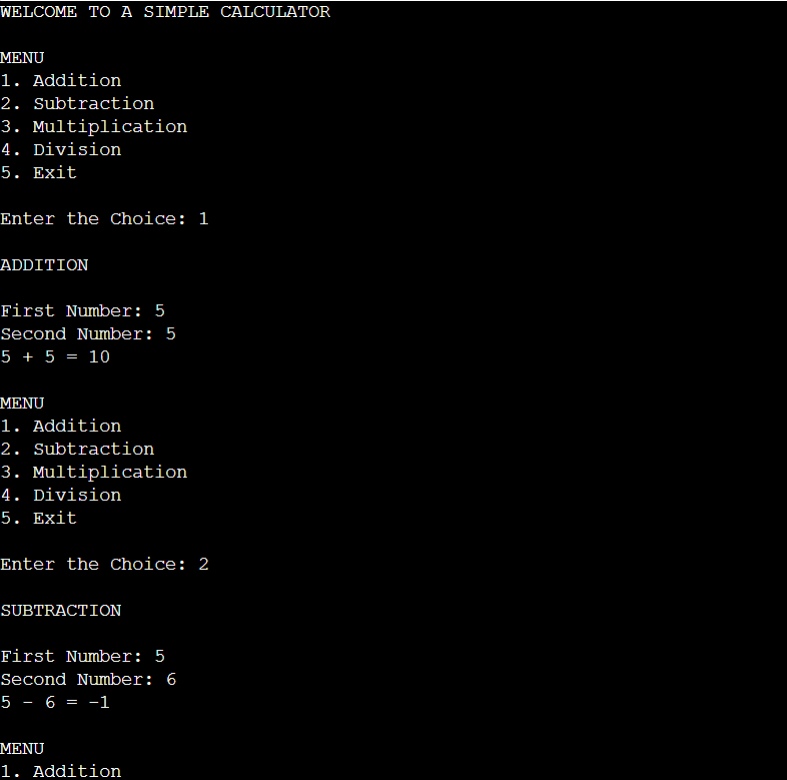
Explanation:
If we write a simple calculator program using c then we use a switch case to perform different operations. But in python, there is no switch case so we’ve to build a calculator using functions or while loops. In this program, we’re writing a program using functions. We’ll do the basic mathematical operations such as Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division. Users have to input 1 to perform Addition Similarly 2 for Subtraction, 3 for Multiplication, 4 for Division.
In the program, the input entered by the user is stored in the choice variable. Then the compiler compares the choice variable with the numbers and the calls the functions. The functions used in this program accept parameters. If we want to calculate the area of the circle then the radius is passed as a parameter to the circle function.
Then the function calculates the area of the circle and prints the area on the screen. If the user enters the wrong choice then the message “Please Provide a valid Input!” is printed. If the user wants to stop the execution of the program then he or she should choose menu option 5.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Menu Driven Program in Python?
Ans: As the name suggests the menu driven program is a type of computer program which accepts the input from the user by showing a list of options. And users have to select any of the options to perform any operation.
What are Menu Driven Programs?
Ans: Menu driven programs are the type of codes that are written in python which accept the input from the user and then perform any task chosen from the menu list displayed.
How do you create a menu based program in Python?
Ans: The menu based program in python can be written using while loops and functions. As the switch case is not supported in python so we cannot write using the switch case.
What is menu driven function?
Ans: The menu driven function is a function that is called when the input entered by the user is matched with the menu option to perform any operation. This menu driven function is parameterized function which accepts the parameters and then performs any task.
Conclusion
In this way, we’ve learned how to write menu driven programs in python using while loop, functions. We’ve written three different programs to clearly understand the menu concept in python. If you have any doubts then please feel free to contact us. We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Thanks and Happy Coding 🙂
Also Read:
- Menu Driven Program in C.
- Fibonacci Series program in python.
- NxNxN matrix Python 3 programs.
- Student Mark Lists Program in Python
![Students Mark Lists Program in Python [Program With Explanation]](https://learnprogramo.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/students-mark-lists-program-in-python-1-500x383.png)
![NXNXN Matrix Python 3 Program [ Program With Explanation ]](https://learnprogramo.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/NxNxN-matrix-python-program-2-500x383.png)
![Fibonacci Series in Python [Program with Explanation]](https://learnprogramo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/FIBONACCI-SERIES-IN-PYTHON-1-1-500x383.png)